Ion chromatograph with autosampler
Ion-exchange chromatography or Ion chromatography is used for analysis of aqueous samples in parts-per-million (ppm) quantities of common anions (such as fluoride, chloride, nitrate, nitrite and sulphate) and common cations (like sodium, potassium, ammonium, lithium, calcium and magnesium) using conductivity detectors. The chroma tography also has the capability to analyze aqueous samples for parts-per-billion (ppb) quantities of hydrazine, monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and unsymmetrical dimethyl hydrazine (UDMH). Ion chromatography is a process that allows the separation of ions and polar molecules based on their charges. The aqueous solution to be injected is usually called a ‘sample’ and the individual separated components are called ‘analytes’. It is often used for water analysis, quality control and protein purification.

Principles of Ion Chromatography:
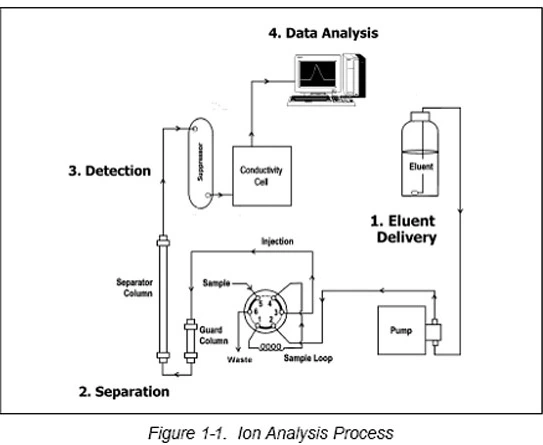
Applications of Ion Chromatography:
- It is used for water chemistry analysis and for detection of chemical contaminants in water especially drinking water.
- It is used to determine sugar and salt content in foods.
- It is used for isolation of select proteins.




